HEALTH + FITNESS
13 Signs You May Have Gluten Sensitivity or Celiac Disease
Published
2 months agoon

Shutterstock
Gluten sensitivity and celiac disease are conditions that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Both conditions share many symptoms, making it crucial to recognize the signs early. From digestive issues to neurological symptoms, these conditions can manifest in various ways. Understanding these signs can help you seek appropriate medical advice and make necessary dietary changes. Here are 13 signs you may have gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
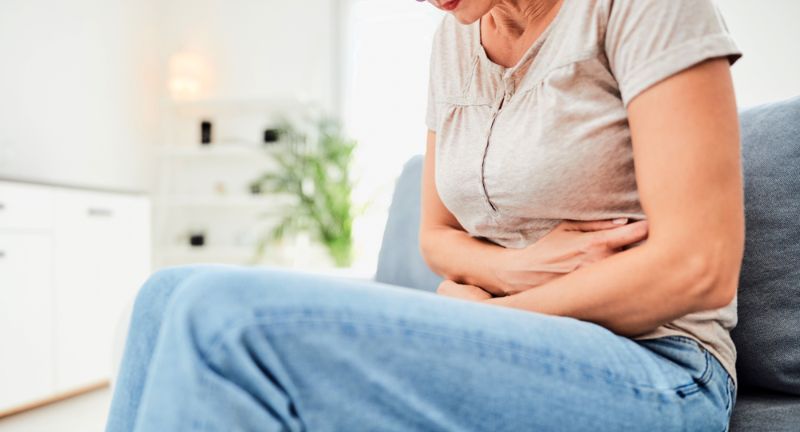
Digestive Issues

Shutterstock
Common symptoms include bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These digestive issues often occur shortly after consuming gluten-containing foods, causing significant discomfort. Persistent digestive distress can interfere with daily activities and overall well-being. Identifying and eliminating gluten from the diet may alleviate these symptoms.
Fatigue

Shutterstock
Persistent fatigue and a general feeling of tiredness, even after adequate sleep, can be a sign of gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. This exhaustion is often due to the body’s inability to absorb essential nutrients properly. Fatigue can significantly impact daily life, making even simple tasks seem overwhelming. Adopting a gluten-free diet may help restore energy levels.
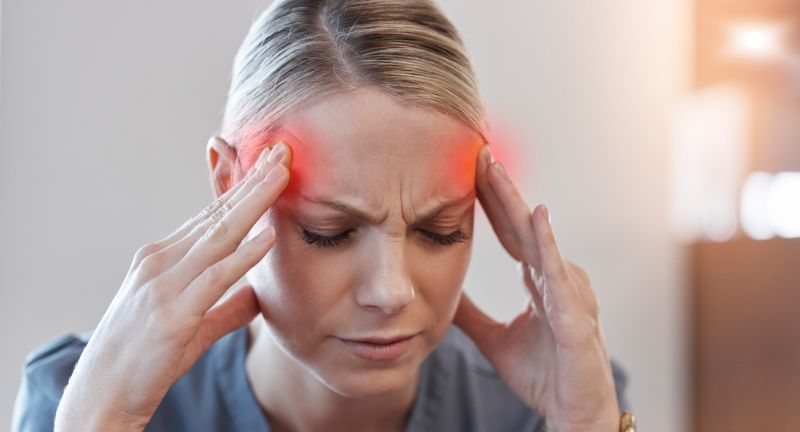
Headaches and Migraines

Shutterstock
Frequent headaches and migraines, especially after eating gluten, may indicate a sensitivity or intolerance to gluten. These headaches can range from mild to severe, often interfering with daily activities. Identifying gluten as a trigger can be crucial for managing and reducing headache frequency. Eliminating gluten from the diet may lead to a significant improvement in these symptoms.
Joint and Muscle Pain
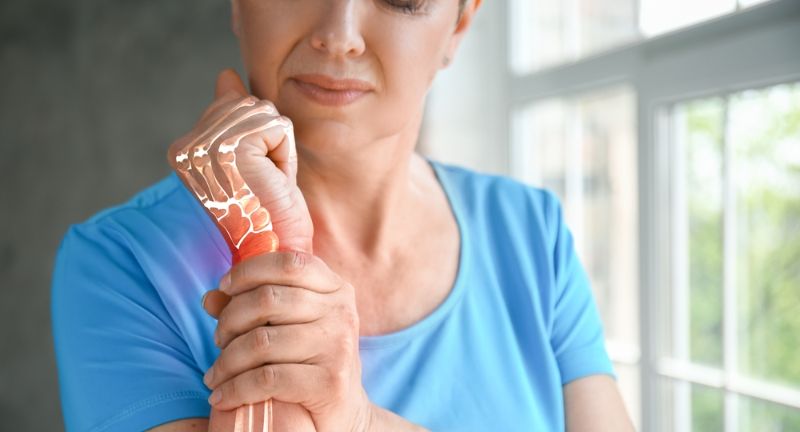
Shutterstock
Unexplained joint pain or muscle aches, not related to exercise or injury, can be associated with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. This pain can be widespread or localized, often causing significant discomfort. Chronic pain can affect mobility and quality of life, making everyday activities challenging. A gluten-free diet may help reduce inflammation and alleviate these symptoms.
Skin Problems
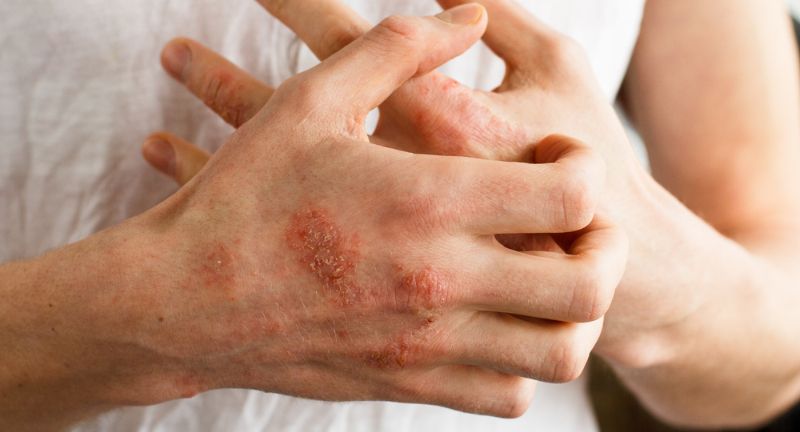
Shutterstock
Conditions such as dermatitis herpetiformis (a blistering skin rash), eczema, and psoriasis may be linked to gluten intolerance or celiac disease. These skin issues can be itchy, painful, and unsightly, affecting self-esteem and comfort. Persistent skin problems might indicate an underlying gluten sensitivity. Eliminating gluten from the diet can lead to significant improvements in skin health.
Mood Disorders

Shutterstock
Anxiety, depression, and mood swings are commonly reported by individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. These emotional disturbances can significantly impact daily life and relationships. Mood disorders linked to gluten sensitivity often improve with dietary changes. Adopting a gluten-free diet may help stabilize mood and enhance emotional well-being.
Autoimmune Disorders

Shutterstock
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder, and having one autoimmune condition increases the risk of developing others, such as type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. These additional autoimmune disorders can complicate the management of gluten sensitivity. Monitoring and managing multiple conditions require a comprehensive healthcare approach. A gluten-free diet is crucial in reducing the risk and managing symptoms of these disorders.
Neurological Symptoms

Shutterstock
Gluten sensitivity can cause neurological symptoms like dizziness, balance problems, and peripheral neuropathy (tingling or numbness in the hands and feet). These symptoms can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Identifying gluten as the cause is essential for managing these neurological issues. Removing gluten from the diet may lead to a reduction or resolution of these symptoms.
Iron-Deficiency Anemia

Shutterstock
Celiac disease can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, including iron, resulting in iron-deficiency anemia. Symptoms of anemia include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin, which can significantly impact daily life. Addressing the root cause of malabsorption is crucial for treatment. A gluten-free diet can improve nutrient absorption and alleviate anemia symptoms.
Weight Loss or Weight Gain

Shutterstock
Unexplained weight loss or difficulty gaining weight can be a sign of celiac disease due to malabsorption of nutrients. Conversely, some individuals may experience weight gain due to inflammation or dietary changes. Weight fluctuations can indicate an underlying issue with gluten metabolism. A gluten-free diet can help stabilize weight by improving nutrient absorption and reducing inflammation.
Reproductive Issues

Shutterstock
Gluten sensitivity and celiac disease can affect fertility and menstrual cycles. Women may experience irregular periods, infertility, or recurrent miscarriages. These reproductive issues can be distressing and impact family planning. Adopting a gluten-free diet may improve reproductive health and outcomes.
Dental Issues

Shutterstock
Dental enamel defects, canker sores, and mouth ulcers can be linked to celiac disease. These dental issues are often seen in children but can affect adults as well. Poor dental health can lead to discomfort and self-consciousness. A gluten-free diet can help improve oral health and prevent further dental problems.
Osteoporosis or Osteopenia
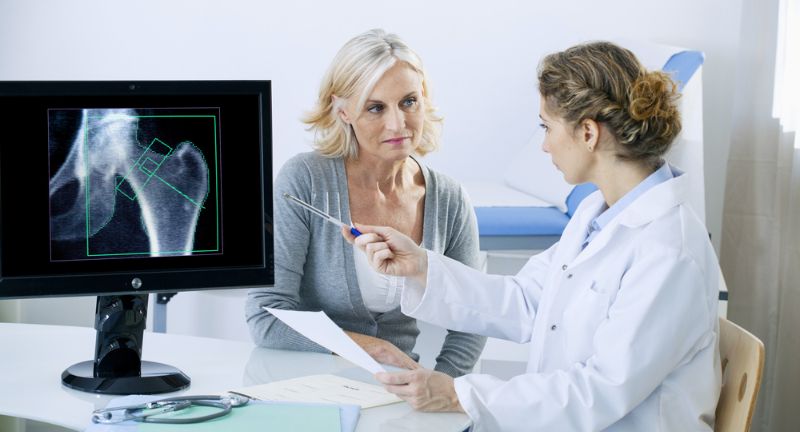
Shutterstock
Due to nutrient malabsorption, especially calcium and vitamin D, individuals with celiac disease may develop weakened bones, leading to osteoporosis or osteopenia. These conditions increase the risk of fractures and bone pain. Monitoring bone density is crucial for those with celiac disease. A gluten-free diet, along with supplements, can help maintain bone health and prevent complications.
Conclusion

Shutterstock
Recognizing the signs of gluten sensitivity or celiac disease is the first step toward managing these conditions effectively. If you suspect you have gluten intolerance, consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis is essential. Adopting a gluten-free diet can alleviate many of these symptoms and improve your overall well-being. Remember, each individual’s experience with gluten sensitivity is unique, and personalized medical advice is crucial. Making informed dietary choices can lead to a healthier, more comfortable life.
Related Topics:

More From Lifestylogy
-


Shannen Doherty Reveals Stage 4 Cancer Diagnosis
-


Starbucks Providing Free Coffee to First Responders
-


Selena Gomez Hospitalized Following Emotional Breakdown
-


Best Bedtime Snacks You Won’t Feel Guilty About
-


30 Fruits That People Are Commonly Allergic To
-


‘Bounty Hunter’ Star in Coma
-


Rebel Wilson Showcases Major Weight Loss
-


How a ‘Worry Journal’ is Helping Simone Biles
-

The Worst U.S. Cities for Mosquitoes – Did Yours Make…